We share many memories with our loved ones, both good and bad. The most beautiful moments feel incomplete without them, and the worst moments are made even harder by their absence. Our lives are enriched by our connections with others, and even ordinary events take on greater meaning thanks to them. In this state of intertwined lives, coincidences such as eating from the same plate or using the same fork and spoon with our loved ones also happen. When sharing a chocolate, for example, the first bite is taken by them and the second by you. After a challenging mountain hike, you might share a bottle of water.
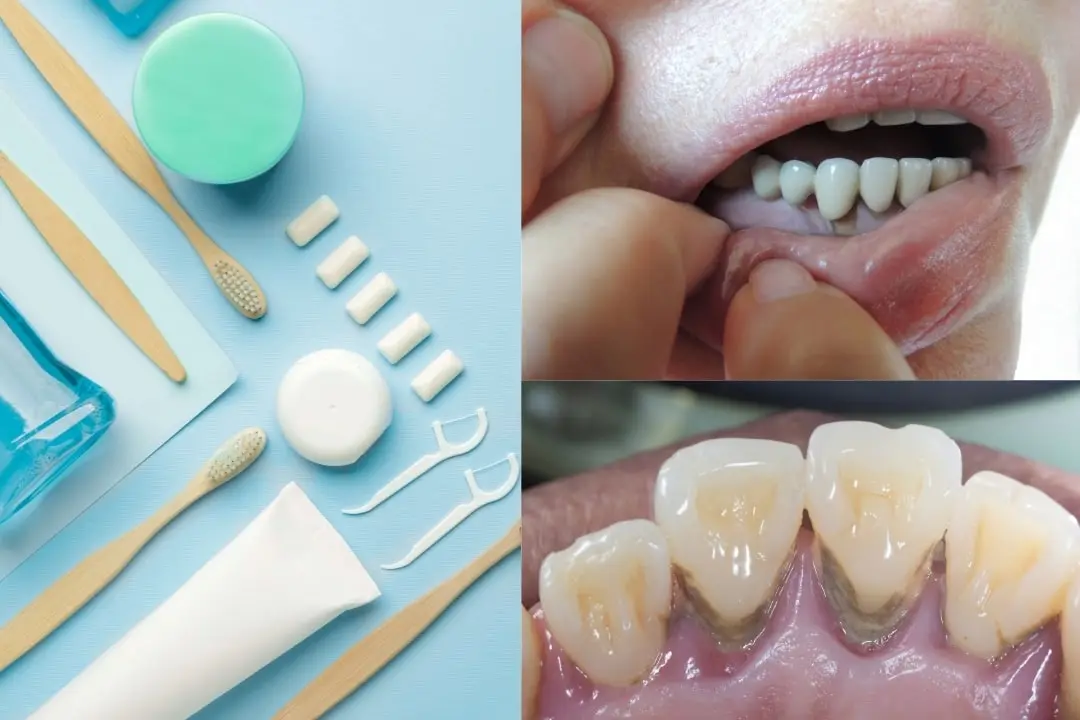
But what if your spouse or friend has a periodontal condition? Is gum disease contagious? More importantly, do you and your loved one know whether you have gum disease? Before we explain all this, we suggest you keep your immunity high and your oral hygiene flawless.
What is periodontal disease and how does it develop?
Periodontal diseases are gum diseases caused by opportunistic bacteria multiplying in the mouth. There are hundreds of types of bacteria that naturally live in our mouths. The vast majority of these species are beneficial. However, some species cause disease. In people with strong immunity who pay attention to oral hygiene and do not consume large quantities of harmful substances such as cigarettes and alcohol, these harmful bacterial species are few and far between. However, in the opposite case, these bacteria can become opportunistic. If no precautions are taken, they cause gum disease.
Common causes of the disease include Porphyromonas gingivalis, Tannerella forsythia, Treponema denticola, and Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans.
An increase in these bacteria leads to gingivitis, the first stage of gum disease. The most striking symptoms of this stage are bleeding, redness, and swelling of the gums. If gingivitis is not treated, it progresses to periodontitis. At this stage, gum recession begins. These recessions expose areas previously protected by the gums to the bacteria. The bacteria then progress from beneath the gums to the tooth root and jawbone. Here, they cause serious tissue loss. Disruption to the balance of oral bacteria leads to an increase in opportunistic bacteria, causing serious infection and leading to tooth and bone loss.
Is periodontal disease be contagious?
Periodontal disease is not contagious. It occurs when the population of harmful bacteria increases among the bacterial species that are also present in the mouths of healthy people. These opportunistic bacteria can be transmitted through sharing utensils, kissing on the lips, or drinking from the same bottle or glass. However, your mouth and immune system are familiar with these bacteria. The conditions that pave the way for the disease include not giving sufficient importance to oral hygiene, having a weak immune system, and being a heavy smoker. In summary, bacteria can be transmitted, but the disease itself cannot.
Myths versus facts about periodontal disease transmission
- Periodontal disease does not spread quickly or directly: Contrary to popular belief, gum disease is not spread through breath or saliva like flu or HPV. However, bacteria in the mouth can be shared through saliva. However, the amount of bacteria transmitted in this way is not enough to cause gum disease. These bacteria are most likely already present in your mouth. The important thing is to avoid turning a small amount of bacteria into opportunistic bacteria.
- Periodontal bacteria settle in our mouths from the external environment: More than a hundred types of bacteria already live in our mouths. The bacteria that cause gum disease are also present, albeit in small numbers, in the mouths of healthy people. However, poor oral hygiene, low immunity, and heavy smoking cause these bacteria to multiply rapidly. This rapid increase causes periodontal disease.
- If one family member has periodontal disease, it does not mean that the whole family has this condition: Living in the same house and coming from the same gene pool does not trigger this condition. An individual with normal immunity who pays attention to oral hygiene will not be affected by this disease.
- Periodontal disease occurs in the elderly: No, gum disease is not seen in elderly people with high immunity who pay attention to oral care and have chronic conditions under control. On the contrary, it can be seen in young individuals.
- Gum bleeding is normal and not contagious: No, bleeding, swelling, and discolouration of the gums are not normal. These are signs of infection. If left untreated, it can lead to advanced gum disease (periodontitis). This can result in tissue, bone, and tooth loss. In such cases, the infected person can only spread the bacteria through saliva. However, if you pay attention to your oral hygiene, the disease will not spread to your gums.
Common signs and symptoms of gum disease
The gums are the soft tissue that protects the root and body of the tooth. They surround the root and body of the tooth close to the gum line. This prevents food residue or bacteria from reaching the root, nerve endings, and bone. However, gum disease destroys this protective barrier. Therefore, gum health is vital for our overall health.
The symptoms of periodontal disease vary depending on the stage of the condition. In the early stage, known as gingivitis, the disease manifests as bleeding, redness, and swelling of the gums. Bad breath is also a symptom. This odour is caused by the acid produced by harmful bacteria in the mouth. If gingivitis is not treated, the condition progresses to periodontitis. At this stage, which is characterised by advanced gum disease, gum recession begins. The gums recede and form indentations. Bacteria then settle in these pocket-like pits. Pain is felt when chewing or biting. There is also a metallic taste and odour in the mouth. Tissue loss occurs in the jawbone and tooth. Over time, teeth may fall out.
In summary, if you experience gum bleeding or sensitivity, we recommend that you see a dentist.
How periodontal disease is diagnosed and treated?
Even if you are experiencing symptoms such as bleeding, swelling, and redness of the gums, the most accurate diagnosis will be made by your specialist dentist. Periodontists are doctors who specialise in gum health. The first examination takes place during your appointment with your specialist doctor. They will examine the colour and shape of your gums. Any bleeding will be observed. The stability of your teeth is tested.
A measuring tool called a periodontal probe is used to check whether your gum pocket is a normal size. In an average, healthy person, the gum pocket is between 1 and 3 mm deep. Greater depth may indicate advanced gum disease.
If periodontitis is suspected, X-rays are used to check for tissue loss in the jawbone and tooth root. Additionally, microbiological tests can identify the bacterial species that cause periodontitis.
Once examination and diagnosis are complete, appropriate treatment should be started quickly. Gingivitis, the early stage of gum disease, is much easier to treat than periodontitis. Methods that can help you achieve the best possible oral and dental hygiene will be shared with you. If present, tartar is removed. If you maintain good oral hygiene by brushing, flossing, cleaning your tongue, and using mouthwash regularly, the disease will regress and disappear.
However, to heal periodontitis, curettage and root surface smoothing procedures are required. Any tartar or dental plaque remaining under the gums is cleaned away. The tooth roots are smoothed so that bacteria cannot settle. The gums are opened and the tissue is cleaned of infection. If there is severe bone and soft tissue loss, a grafting procedure is performed to compensate for this. Antibiotics are used to support the treatment if necessary.
Measures to prevent spread and protect your gums
Good oral hygiene is essential for healthy gums. Teeth should be brushed at least twice a day. Brush the upper teeth from top to bottom and the lower teeth from bottom to top. Each tooth should be brushed carefully during brushing. Use a soft or medium-hard toothbrush. The spaces between the teeth should be cleaned with dental floss or an interdental brush. When brushing or cleaning between teeth, you should always be gentle with your gums. Hard movements that may cause bleeding should be avoided. The tongue has surfaces that can lead to bacterial growth. For this reason, we should clean our tongue with a toothbrush or a special cleaning tool. Finally, the whole mouth should be rinsed with mouthwash.
Regular doctor check-ups are recommended. This allows any issues to be noticed early and treated promptly. In addition, regular tartar removal is important for oral and dental hygiene.
A diet rich in vitamin C and calcium and having strong immunity are beneficial for oral and dental health.
Smoking harms the gums.
Sugary foods increase bacterial growth. For this reason, excessive sugar consumption is best avoided.
When to seek professional advice for gum health?
Firstly, bleeding gums are the first sign of gum disease. If you also notice redness, discolouration, or swelling of the gums, we recommend that you see your dentist. If you notice gum recession or loosening of the teeth, as well as a metallic odour or taste in your mouth, you may have advanced gum disease. You should seek help from your dentist as soon as possible to prevent further damage.
FAQs
Can hormonal changes affect gum health?
Our hormonal balance can directly affect gum health. Puberty, menopause, and menstruation can make the gums sensitive. During these times, it is important to pay more attention to your oral hygiene routine.
Does diet impact periodontal health?
The diet and habits are among the factors that directly nourish gum health. While sugary and acidic foods and drinks negatively affect oral health, foods rich in vitamin C, calcium, and protein positively affect tooth and gum health. However, no matter what we eat, it is very important not to neglect oral hygiene.
Can stress influence gum disease?
It is a well-known fact that stress has a negative effect on the immune system. During these times, we become much more susceptible to the adverse effects of viruses and bacteria. This is why stress lowers our immunity and allows opportunistic bacteria to proliferate.
