Do toothaches cause ear pain?
Yes, toothache can cause earache.
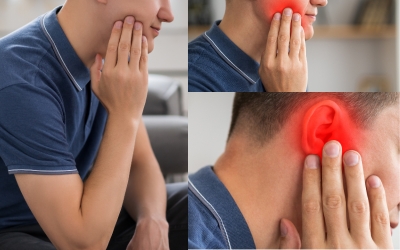
Since the teeth and ears are connected by the nerve network of the face, pain from a tooth can be referred to the ear, especially if it originates from the teeth in the lower jaw. This type of referred pain occurs when nerves such as the trigeminal nerve are affected, and this can cause the toothache to be perceived as pain felt in the ear.
For example, a tooth abscess, cavity, or gum disease can cause pain not only around the tooth, but also in or around the ear. An abscessed tooth is especially at the forefront of toothaches. If left untreated, it causes swelling and pain towards the ears and jaw. If the infections caused by the pain spread to the heart or brain, it can also be life-threatening.
In this context, a problem caused by a tooth can sometimes be considered an ear infection. In such cases, it is critical to see both a dentist and a doctor to determine the source of the pain and get the appropriate treatment.
No one expects to have a toothache. It can happen at the most inconvenient times and cause a lot of pain. A person should see a dentist when they have a toothache. If you have pain that radiates to your head or ear at the same time as your toothache, please contact our aesthetic dental clinic in Antalya and make an appointment immediately.
Toothaches and earache
A toothache is defined as a sharp and often uncomfortable pain felt in the tooth or surrounding tissues. This pain can range from a short-term sensitivity to a long-term, unbearable ache. Toothache is usually associated with irritation of the nerve of the tooth, and the factors that cause this irritation can be caused by a variety of conditions, such as tooth decay, infection, gum disease, a broken tooth, or inflammation of the tissues around the tooth.
The severity and duration of the pain can vary depending on the underlying cause. In some cases, the pain can spread to other areas, especially nearby areas such as the head and ear.
A toothache is a condition that usually worsens over time, and therefore it is important to treat it quickly. If left untreated, the infection inside the tooth can spread and lead to more serious health problems. Therefore, it is recommended that a person with a toothache see a dentist as soon as possible.
Earache is an uncomfortable condition felt in the ear or surrounding structures. It usually occurs as a result of otitis media, external ear infections or blockages in the ear.
The difference between earache and toothache
Symptoms of earache include ear infections, fluid buildup behind the eardrum, or problems with the ear canal. The pain from earaches is usually deep and sharp, sometimes accompanied by hearing loss, a feeling of fullness in the ear, or even dizziness.
A toothache is usually caused by dental problems such as cavities, gum disease, or an abscessed tooth. Pain in or around the tooth, and pain after eating hot or cold foods may occur.
Therefore, the safest way to determine the cause of your earache is to make an appointment with our Acardent Turkey Dental Clinic.
What causes ear and jaw pain?
Temporomandibular Joint (TMJ) Disorders:
Dysfunction in the joint that connects your jaw to your skull can cause pain in both the jaw and the ear.
Ear Infection (otitis media):
An ear infection can cause discomfort in and around the middle ear, which can also spread to the teeth.
Dental Problems:
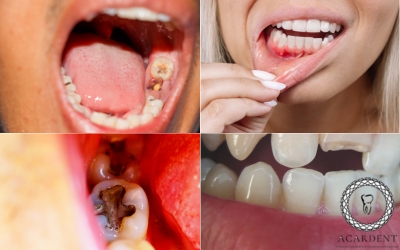
Oral and dental health problems such as tooth infections, abscesses, and gingivitis can cause discomfort in the ear and jaw.
Sinus Infection:
Sinus infections and inflammations can put pressure on the teeth and ears and can be uncomfortable.
Bruxism (teeth grinding):
Grinding or clenching your teeth can put stress on surrounding tissues, including the jaw and ear, causing your muscles to tighten and cause discomfort.
Jaw Trauma or Injuries:
Trauma or direct damage to the jaw can cause pain to radiate to the ear, and such conditions require medical treatment.
Symptoms of toothache and earache
Symptoms of toothache and earache are generally as follows:
Symptoms of toothache
- Sensitivity to cold or hot foods.
- Increased pain in the teeth while chewing.
- Constant throbbing or sharp pain in the tooth.
- Inflammation, swelling or redness in the gums.
- Bad taste in the mouth or foul-smelling breath.
Earache symptoms:
- Hearing loss or muffled sounds.
- Increased pain in the ear with jaw movement.
- Discharge from the ear.
- Dizziness or loss of balance.
- Throbbing around the ear.
Is there a link between toothache and earache?
Dental health can significantly affect earaches due to the connection between the nerves in the teeth and ears. Problems such as cavities, gum disease, or tooth abscesses can cause referred pain that feels like an earache when the problem is in the mouth. The trigeminal nerve, which serves both the teeth and the ears, transmits pain signals that can often be confusing to pinpoint.
Maintaining good oral hygiene and detecting dental problems early can help prevent earaches related to dental problems. It is important to see a dentist if you are experiencing ear or tooth discomfort.
Toothache and ear pain in the same side
Toothaches and earaches that occur on the same side are often linked because the nerves in your face, teeth, and ears are tightly connected. When your tooth becomes infected or inflamed, the pain can radiate and cause discomfort in the ear as well. This is especially common with problems such as cavities, abscesses, or impacted wisdom teeth. It is important to get dental care promptly to heal quickly and prevent further complications.
How to relieve ear pain from toothache
- Apply a cold compress to the painful area with an ice pack and relieve the pain.
- Pay attention to oral hygiene, brush your teeth regularly and use dental floss.
- Massage the gums with clove oil to relieve toothache
- Relax the muscles by applying a warm cloth compress around the ear.
- Gargle with salt water to clean the bacteria in the mouth and reduce the pain.
- Try to relieve the pain by using painkillers and if the pain does not go away and starts to increase, it is important to see a dentist.
